
XR or Extended Reality is an umbrella term for all immersive technologies and its variants such as VR, AR and MR. There is no separate technology called XR and the ‘x’ in XR could stand for any letter.
| Virtual Reality (VR) | Augmented Reality (AR) | Mixed Reality (MR) |
|---|---|---|
| VR is an entirely digitally created or filmed synthetic world which disconnects the user from the physical environment. | AR is the hybrid of Physical and Digital worlds where contextual 2D infographics are overlaid on top of the physical world. | MR is the hybrid of Physical and Digital worlds where contextual 2D & 3D infographics are overlaid on top of the physical world with 3D depth and spatial understanding. |
| VR is completely immersive with 180 or 360-degree field-of-view visuals. | AR is visually less immersive compared to VR. | The immersion of MR falls between VR and AR. |
| VR is experienced through Head Mounted Devices. | AR is experienced with the use of handheld devices such as a smartphone, tablets or AR wearables. | MR is experienced through Holographic See-through or Pass-through Wearable Goggles. |
| User interactions inside this virtual world are through Gestures, voice commands and Hand-Controllers. | User interactions inside AR are through touch inputs and voice commands. | User interactions inside MR are through hand gestures and voice commands. |
| VR is mainly used for various training and simulation purposes. | Apart from classroom training, AR is mainly used for on the job guided assistance and remote support while performing tasks at manufacturing plants. | Apart from classroom training, MR is also used for on the job guided assistance and remote support while performing tasks at manufacturing plants. |
| VR can be used only inside an Indoor safe environment such as classrooms and office rooms. | AR can be used both only indoor and outdoor environments and allow the user to move around safely and experience both the real and digital worlds that are presented. | MR can be used both indoor and outdoor environments and allow the user to move around safely and experience both the real and digital worlds that are presented. |
Yes, there are hands-free alternatives such as Head-Mounted Tablets (Realwear HMT) and smart glasses like Vuzix. Though these wearables are not very immersive or rich in 3D graphics, they provide instant assistance while performing jobs with a hands-free experience. Since there is no spatial tracking of the environment, the experience is limited only with context sensitive heads up display (HUD), usually triggered through markers & QR codes.
VR technology can be experienced in many ways. It depends on the solution being developed, performance, user interaction, VR content and experience desired in the virtual worlds. Fusion VR understands these requirements and recommends the devices for sustained high performance using this immersive technology.
The first is PC powered VR where heavy complex 3D assets and interactions are involved and the required processing happens at PC. The devices in use are typically Oculus Rift and HTC Vive categories.
The second type is the Standalone VR which is ideal for watching VR movies and simple gameplay. The processing and storage are internal and the most common devices for such applications are Oculus Quest and Vive Focus categories.
The final type is the VR-Box which uses mobile phones that are inserted inside the box like Google cardboard or Samsung Gear VR. Such devices are entry level, that give a basic demonstration of VR experience for the first-timers.
Interactive video enables movement and activity in a fully immersive environment, while VR video delivers passive engagement in the same environment. Interactive VR headsets provide 6 degrees of freedom (6DoF) compared to VR video headsets which offer only 3 degrees of freedom (3DoF). The ability to rotate your vision in all directions or axes (X, Y and Z) while sitting in one position is 3 DoF, while the ability to also move back and forth along all three axes is 6DoF. There is unrestricted movement and vision in all three axes with an interactive VR experience.
Passive VR videos can either be a capture of real places using special VR camera rig setups or a graphic render of 3D modeled environment. In both cases, here are the typical variants, its characteristics and our recommendation:
I. The primitive “180-degree monoscopic” VR videos give a narrower 180 degrees field of view without any reference for spatial depth and objects’ scale - Very poor experience; No immersion; Not recommended.
II. The entry level “360-degree monoscopic” VR videos give a wider 360 degrees of field of view without any reference for spatial depth and objects’ scale - Poor experience; No immersion; Not recommended.
III. The professional “180-degree stereoscopic” VR videos give a narrower 180 degrees field of view but with accurate representation of spatial depth and objects’ scale - Very good experience; Highly immersive; relatively economical to produce. Strongly recommended since this optimized format effectively utilizes the full potentials of the current VR hardware and software players.
IV. The professional “360-degree stereoscopic” VR videos give a lifelike 360 degrees field of view with accurate representation of spatial depth and objects’ scale - Ultimate experience; Truly immersive; Not recommended at least for now since the current VR hardware and software do not have adequate efficiency to render this format in its fullest quality. Soon the situation will change though.
Industrial training module simulation typically involves real-time user interactions, heavy graphics and complex analytics which requires more memory and greater CPU-GPU processing power and speed to deliver the minimum fps and resolution. In order to deliver the optimal performance on resolution, FPS, latency, physics simulations, fluid simulations, realistic lighting calculations etc., definitely an external workstation is needed to power the VR headset.
Standalone VR devices currently in the market do not possess the required processing power to meet performance criteria and specifications of high quality VR.
As explained above, standalone devices such as Oculus Quest would not be able to meet the demanding requirements of industrial simulations. For such applications and similar virtual content, more powerful PCs would be required.
VR training modules can be hosted remotely, but the experience is highly dependent on the data transmission bandwidth and latency to provide a comfortable user VR experience in the VR environment. The current 4G speed & latency may not permit that now but is certainly within our reach with the availability of 5G enabled standalone VR devices and deployment of 5G networks and associated infrastructure.
Unfortunately, the answer is “Yes”. The two major factors affecting cloud VR are Network Speed & Latency which the current 4G lacks to meet the minimum specifications. Please note, apart from 5G network & infrastructure, one also needs a 5G supported VR device which is expected to be launched only in 2021. If you are interested in knowing more, here are the detailed calculations & facts comparisons.
Bandwidth: VR video with separate full HD displays for left & right eye has effectively 2.6 million pixels (1080pix X 1200pix X 2 displays) which needs a download-throughput of 100-150mbps @ 90fps.
Estimated Bandwidth for a compelling VR experience: 100-150 Mbps
Bandwidth of current 4G networks: Theoretical 300 Mbps; Real-world 20-30 Mbps
Bandwidth of 5G networks: Theoretical 10-50 Gbps+ / Real-world 150 Mbps - 1 Gbps+
Latency: Poor latency typically affects the 6DoF interactive VR experiences as reasoned below.
a) Round Trip Time (RTT) is the time taken for user actions from the VR device to reach the cloud, processed and received back at the device, which effectively relies on the network Latency.
Recommended Latency for a compelling VR experience: 5-10ms
Minimum latency for an acceptable VR experience: Not more than 20ms
Latency of current 4G networks: 50ms
Latency of 5G networks: Theoretical 1ms; Expected Real World 10ms
b) Video Compression: Quality of video compression and encoding speed on the cloud computer has to be adjusted according to the network latency. While using the 4G network with poor latency, the video quality will be compromised to achieve the lowest possible latency.
Note: The above estimations are based on the reports from various sources. The objective is to explain the constraints of 4G over 5G in view of Cloud VR implementation.
AR Goggles provide simple text & infographics overlays, augmented on top of the real world you see in front of you. Information is triggered using external markers or QR codes placed in the environment. Displayed information will be in a heads-up display (HUD) style which won't be immersive.
MR Goggles provides rich 3D graphics as holographic overlay inside the physical space of the real-world. The environment & object tracking capabilities of the device eliminates the need for any kind of external markers to trigger info. The spatial awareness and memory capabilities of MR Goggles let you experience the physical world in front of you in a much richer way through context sensitive information and interactive 3D graphics.
AR devices such as Realwear HMT-1Z1 are certified as Intrinsically Safe (IS) which are truly safe for use in hazardous environments. Such areas are defined by the Class/Division or Zone system and IS devices are identified appropriately. Such devices are safe to use as they do not generate energy that could ignite a hazardous mixture.
As of now, we haven’t come across any IS certified MR devices.
Internet connectivity is not necessary when taking AR assistance for standard instructions and SOP guidance while working inside a plant, since the internal memory of the device can store the necessary data.
In case of remote support such as video call is required to troubleshoot an ongoing issue or when live data from DCS, SAP to be seen for decision making, then internet connectivity will be a must.
In practical sense, existing 3D-CAD models can only serve as reference while recreating the physically accurate digital twin of an existing plant environment. These CAD models are technically built upon mathematical faces & surfaces such as “NURBS”, while 3D models for VR engines require a geometrical mesh composed of “POLYGONS” or “TRIANGLES”.
Direct conversion of NURBS to POLYGONS ends up with extremely heavy models with no option for photorealistic textures and lighting which defects the whole purpose of creating an immersive VR environment. Certain optimization techniques on top of the converted model may work in a few cases. But, natively recreating the polygonal surface models ground up using software such as Maya, 3DS Max & Blender gives the best output and highest VR rendering.


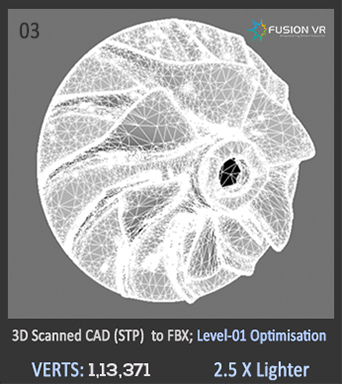
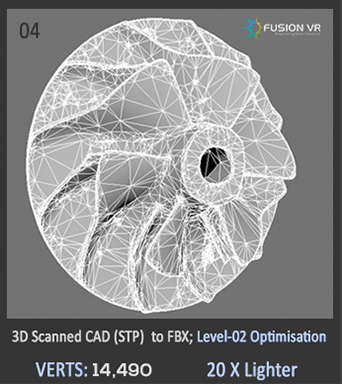






Not having 3D CAD models is not a major problem. The best option is 3D Scanning of the equipment and plant units which is quite accurate and to scale. We can also create representative 3D models using photographs, general arrangement drawings of vessels/equipment and piping (Such as PFDs & P&IDs) to fulfil the technical and functional requirements of the solution designed.
Such conversion is possible, but the results achieved may not be what you desire. VR models are created with relatively more details (Heavy) because they are optimized for the powerful external PC, while AR models and their digital objects are created with less details (Light-weighted) since they are optimized for the limited computing power of the inbuilt mobile processors.
Take for instance conversion from VR to AR in which the application would be quite heavy for a mobile device and will require significant optimization otherwise the AR experience will suffer. On the other hand, a conversion from AR to VR, you would find that the details of AR models are not really adequate enough for rendering a high-quality VR experience.
Absolutely. Fusion VR is a dependable and trustworthy partner when it comes to respecting Intellectual Property (IP) and the custody of sensitive and confidential client information. We have handled and delivered defense & other international projects through NDAs with successful outcomes.
Unfortunately, this is not possible as considerable resources cannot be deployed to site. Also, the developmental work on any project requires the collaboration of several different disciplines and stakeholders. Product development and testing is at Fusion VR facilities while final deployment and site testing occurs at the client/end-user location.
The product owner is always the client. Your design will remain your intellectual property (IP). Our innovations, ideas, processes, codes, artworks and tools will remain our IP.
No, we do not represent any specific OEM or brand. We are open to all devices and manufacturers. We have vast experience in developing content for all major Extended-Reality devices such as Oculus-Rift, HTC Vive, Microsoft HoloLens, Real wear-HMT, Android and Apple Devices. But we always recommend appropriate devices according to use case and optimal experience for our clients as we have been in this industry since its inception.
All our VR, AR, MR solutions use commercially available off-the-shelf hardware and devices. Other custom-made smart solutions which involve technologies such as Computer vision, IoT, etc. might require customizable devices for which Fusion VR would provide the appropriate professional advice for successful implementation of the project.
The typical timeline for the development of any Extended Reality solution is approximately three (3) months. It also depends on the scope and its performance requirements. The testing and other finishing processes depend on several factor
Our goal is to be open and transparent with our clients and always strive to deliver a product or solution at the quickest possible time frame without compromising on our quality and performance standards. Though budgets vary greatly according to final scope, we can give ballparks upon understanding your basic requirements.
Yes. We have expertise in undertaking small projects for developing POCs and providing a demonstration before taking on the actual project for your organization. The POC would be a cost-plus project as considerable expertise and resources need to be invested to produce the POC. In most cases, we waive-off this POC cost from the final invoice of the actual project billing as a token of goodwill.
Firstly, Fusion VR is an Industry 4.0 solutions company with a team of engineers, scientists, HSE Experts and operators with more than 25 years of industry experience who understand the pain-points & ground-reality of the high-risk process & manufacturing plants.
Secondly, while most competitors struggle to understand the scope of work (SOW) given by clients, we extend our support to help you draft the SOW. We speak the manufacturing language and understand what our client needs, to effectively and cost efficiently implement projects to overcome the challenges.
Finally, we empathize and care about the future of our clients. The living proofs are our “Testimonials” from our satisfied clients and partners with a decade of relationships.
We guarantee the performance of XR software for 12 months for the intended hardware which was originally developed for. Second year onwards, you can signup for AMC (Charges varies from 7 to 16% of the original project cost depending on complexity and duration of the AMC period).
This covers any issues/bugs araises post OS Updates, device SDK/Drivers/Firmware updates.
Software Upgrade: In case of additional features and modifications on existing software are requested, we will work out the quote based on the efforts to be rendered.
Hardware Upgrade: If you plan to upgrade/switch to new hardware when the existing device becomes obsolete, software update/porting will be required for the application to run smoothly. There will be nominal porting charges involved on Case-to Case basis.
 Voice Enquiry
Voice Enquiry

 Get Started
Get Started