Augmented reality (AR) has impacted the face of education sector, bringing to it very immersive learning experiences that have placed it in the middle between the traditional and digital learning experience. Trends in courses about augmented reality are beginning to gain momentum in 2024; this marks transformations in classrooms, excitement among students, and deeper understanding. As technology advances more dramatically day by day, augmented reality training courses have gained their value and usage in education. They are no longer a wonder but a must implement in order to provide novel ways of engaging content for interaction.
Evidently, the most significant trend shaping the role of AR in educational structure is interactive learning environments. Unlike other passive modes of learning that rely more on memorization, AR courses engage the learner actively. Abstract ideas become real because digital information is overlaid onto the physical world. For example, while studying the solar system, students will not only view planets in 3D, they also experience it in real-time, move them around and bounce them off each other to better understand and remember the related information. This level of interaction creates more dynamic learning environment and helps students become active participants, rather than usual spectators.
The other significant trend is the personalized learning experiences offered by AR courses. As every student learns differently, the conventional classroom settings cannot accommodate these varied learning styles most of the time. Augmented reality training courses can easily provide for customization of learning materials according to the needs of each student. Through the use of AR-based applications and learning systems, learners can access their customized lessons, tutorials, and exercises that harmonize with the self-learned processes. The positive attribute here is that no one falls behind because that kind of openness propels an open learning system where everyone can grow through learning.
Collaborative learning with the integration of AR is becoming even more prominent. Group activities in a traditional classroom may be limited by logistics or available resources. It is these deterrents that AR courses eliminate. In an AR setting, students can work cooperatively regardless of where they are geographically located. Whether it be a science experiment or history project, students can share real-time, deeply immersive experiences to learn teamwork and problem-solving skills. This collaborative nature of AR fosters communication between students and prepares them for the interdependent world that they will face in their professional careers.
AR is very effective in blending the physical and digital worlds and is a very strong application in the realm of STEM education. Substances such as chemicals in chemistry, physical phenomena in physics, and biological phenomena in biology are usually taught using experimentation. To understand such content accurately, lab or experimental study is a must. An advantage of AR courses is that students can conduct virtual experiments similar to those in a real world to avoid cost and danger. This trend is highly imperative in schools that lack the wherewithal to fully provide laboratories. The AR can be used for students to learn about chemical reactions, dissect virtual organisms, and build engineering models in an entirely interactive immersive environment.
Applications of AR in remote and hybrid learning is another trend that cannot be overlooked. The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in a massive shift that has experienced seismic shift in the way of delivery of remote education. More engaging and interactive online learning tools in greater scale were needed by people immediately after the change. Augmented reality courses create such needs where such immersive experiences can be accessed anywhere. AR brings comfort to the confines of students’ homes by allowing them to engage with 3D models, interactive simulations, and even virtual field trips. This evolution provides the least shift from a face-to-face and remote teaching gap while making sure students learn material good enough for wherever they might end up.
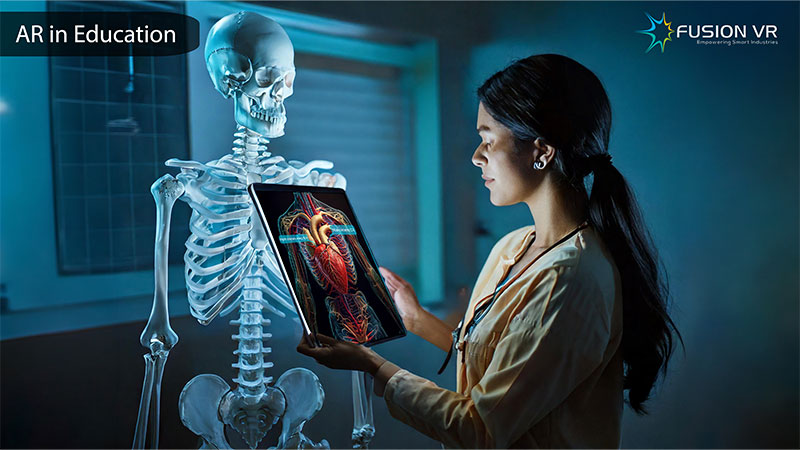
In vocational training and higher education, AR courses are highly adapted to offer live, real-time hands-on experience in health care, engineering, and architecture. For example, medical students may use AR to learn anatomy 3D, practice surgery, or view anatomical structures without having corpses. Meanwhile, the engineering students can use AR to visualize and understand intricate machines, while the architecture students can “walk through” virtual designs. This trend is changing the face of how practical skills are delivered to students, giving more insight into their chosen fields and preparing them better for the workforce.
Augmented reality has also been making new waves in the training and professional development of teachers. Educators use the AR training courses to refresh their teaching tools and have more engaging lessons that work for the betterment of their students. Teachers can try different teaching methods and approaches with the help of AR by mimicking classroom settings. This trend is generally in tandem with the idea of continuous professional development as this keeps educators abreast of the latest technological advancements and innovative pedagogies.
Advancements in AR provide more opportunities for instruction outside the classroom. Augmented reality courses are now being implemented by museum, cultural, and corporate training programs. It opens doors to lifelong learning opportunities between students and professionals. It infuses learning into exploration, allowing students and professionals to learn AR-powered experiences within real-world settings. For instance, museums can use AR to present interactive exhibits that can bring historical artifacts to life. Companies can use it as a source to train their employees to accomplish difficult tasks or procedures. This, in turn merges the lines that distinguish formal from informal learning towards a much holistic experience.
The reasons that compel the adoption of AR in education continues to rise with the growth of the partnership between educational institutions and technology companies. The alliance programs like Fusion VR’s Industry-Academic Alliance Program alone make the difference in the delivery of augmented reality courses to schools, colleges, and even universities. These collaborations, hence, allow the provision of the wherewithal in terms of tools, resources, and expertise that will deliver effective AR within curricula. Such an arrangement empowers educators to take full advantage of the education-enriching features of AR, which brings the learning environment into a proper interaction with students prepared to contest the challenges of the 21st century.
Much promise does the future of augmented reality in education hold: from further innovation breakthroughs in technology and pedagogy toward even more applications. Augmented reality training courses will surely reach more people, making it accessible to the lower rungs of the educational ladder, from primary schools to universities and vice versa. The trends we are witnessing portend a much larger revolution in the way teaching and learning are approached.
Thus, augmented reality does not mean merely a way of enriching education; instead, it transforms the learning face itself. Courses will be interactively, personally, and collaboratively designed to make students think critically and work creatively, and students will have greater insight into harder topics. As we journey into 2025, the trends of augmented reality training courses will continue to evolve and trend, resulting in greater innovation and new opportunities for students and educators alike. The future of education is no longer digital but also immersive and interactive, truly engaging, especially in the wake of initiatives like the Industry-Academic Alliance Program by Fusion VR.